My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
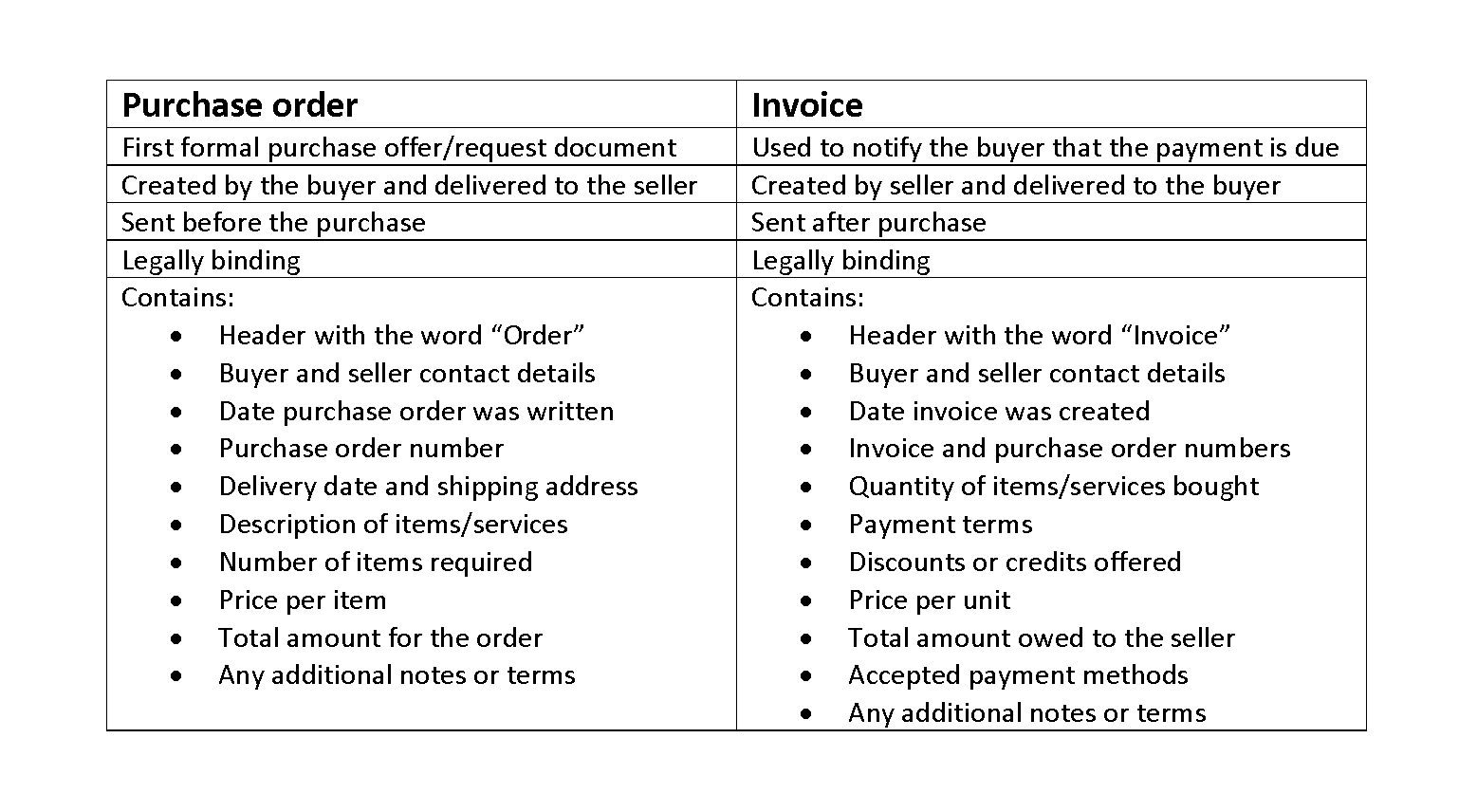
What Are Control Accounts?
- E.g., it may be a separate account designed for vendors and maintained, which summarizes the personal accounts.
- Control accounts are part of double-entry accounting, which states that any debit posted to the general ledger will have a corresponding credit posted to the general ledger as well.
- The reason these accounts are called control accounts is because one uses them to ensure there are no errors or mistakes in our records relating to debtors and creditors.
- Control accounts refer to general ledger accounts that summarize the detailed transactions from a subsidiary ledger or individual accounts.
- This section will look at the transactions for Fooz Ball Town and how to post to subsidiary ledgers for accounts receivable and accounts payable.
However, if Taylor or anyone else wants to find out the amount that a specific customer still owes for their credit purchases, or when they bought the item, that won’t be shown in the control account. Jim doesn’t need to post the details of any of the transactions since the details are already recorded in the subsidiary ledger. Using a control account can guard against fraud, particularly if you have someone else maintain the control account. For example, if your bookkeeper or accounting clerk is responsible for entering sales or purchases transactions, you can have someone else be in https://www.bookstime.com/blog/difference-between-daybooks-journals-ledgers charge of the control account, thus providing a safeguard against fraud. For example, if the sales account balance is transferred, the sales account will be debited, and the sales control account will be credited. The control ledger is the summarized account maintaining the records of individual accounts involved in the ledger, and the same is clarified and re-verified.
Understanding Goodwill in Balance Sheet – Explained
The ending balance in a control account should always match the ending total for its subsidiary ledger. If it doesn’t, then there could have been a mistake made during the calculations. For more details regarding each of these subjects, you’ll have your subsidiary ledger. Here you’ll find specific details like how much a customer still owes, or when purchases were made. If you’re still using manual ledgers to record accounting transactions, the best thing you can do is make the switch to accounting software, which includes complete control account management.
Related AccountingTools Courses
The only real issue control account example with a control account is that it forces anyone investigating a transaction to shift down to the referenced ledger to find the transaction in question. This can slightly increase the time required to investigate a transaction, but it is not a critical concern. A control account can keep a general ledger from becoming choked with transactional detail.
Understanding Control Accounts: Essential Guide for Beginners
When monitoring your business’s general ledger, you may have an accounts receivable control account. The control account will only show you the accounts receivable balance after all calculations have been done. It will include end amounts for things like total credit sales, collections from customers, and the total amount still owed. When reviewing the control ledgers, it’s easy to identify errors that exist in subsidiary ledgers. Because the control account only reviews the end balance, there is less risk of miscalculation.

The two main transaction types for accounts receivables are credit invoice sales transactions, and the receipt of cash from customers. Control accounts speed up the process of producing management accounts information as the control account balance can be used without waiting for the individual balances to be reconciled and extracted. The subsidiary ledger allows for tracking transactions within the control account in further detail. Individual transactions appear in both accounts, but only as an ending balance in the control account. More details such as where the money came from, who it came from and the date it was paid appear in the subsidiary ledger.
Company
- By maintaining accurate balances in the general ledger, control accounts facilitate efficient financial management, monitoring, and reporting.
- Planning packages are typically used to define the work that will be performed during a specific phase of the project.
- In a larger business, where the transactions are too many to be managed by one person, subsidiary ledgers such as the accounts receivable ledger (sales ledger) and the accounts payable ledger (purchase ledger) will be opened.
- The cash receipts are posted to the debit side of the cash control account, and to the credit side of the accounts receivable control account.
- The ending balance in a control account should always match the ending total for its subsidiary ledger.
Hence, we have reconciled the balances and can use this balance in the preparation of financial statements. With the double-entry accounting system, accounts receivable, and accounts payable are the common types of control accounts. Smaller companies may be able to rely on control accounts if they remain balanced using double-entry accounting. With accounts receivable, as invoices go out the control account is debited, which increases the balance. And as payments come in, the control account is credited, decreasing the balance.

What is the Purpose of Control Accounts?
We need to apply control because these accounts are expected to have a massive number of transactions. Each party’s total is accumulated at one place, and a certain balance is calculated to be used in the trial balance for the formation of financial statements. Check your understanding of this lesson by taking the quiz in the Test Yourself! And right at the bottom of the page, you can find plenty more questions on control accounts submitted by fellow students. When a customer makes a payment for an outstanding invoice either a https://x.com/BooksTimeInc check will be received or if paid directly to the bank account, an entry will appear on the bank statement of the business. The check and the bank statement are both source documents in relation to the cash receipt transaction.


